Difference Between Conservation Law In Peninsular And Sabah Sarawak
The main land law governing land ownership and tenure in Peninsular Malaysia is the National Land Code 1965 NLC which came into effect on 1st January 1965.
Difference between conservation law in peninsular and sabah sarawak. The National Land Code Penang and Malacca Titles Act 1963 regulates land tenure in the states of Penang and Malacca only. Sabah Sarawak Labuan Federal Territory 1. Fair Representation We will increase national integration between Sarawak Sabah and Peninsular Malaysia through a fair power-sharing arrangement that fully upholds the spirit of the Malaysia Agreement.
The Sabah Land Ordinance and Sarawak Land Code respectively. Business license not required required required required 3. East Malaysia lies to the east of Peninsular Malaysia the part of.
The two ordinances are virtually similar in contents. The earliest human settlement in Sabah can be traced back to 2000030000 years ago along the Darvel Bay area at the Madai-Baturong caves. Advertisement Pre-approval from state government not required required required not required 4.
The Sabah Land Code Cap 68 regulates land tenure in Sabah whilst land tenure in Sarawak is regulated by the Sarawak Land Code Cap 81. PART I PRELIMINARY Short title and commencement. Sabah came under the influence of the Bruneian Empire in the 14th and 15th centuries while the eastern part of the territory was given to the Sultanate of Sulu because.
Sabah and Sarawak have their own sets of laws. Otherwise Malaya is still more equal than Sabah Sarawak. It consists of the Malaysian states of Sabah Sarawak in the west and the Federal Territory of Labuan.
In a disturbing development recently some tour operators have even started offering private bushmeat dinners for foreign tourists in Sabah. Many people are at a lost as to why Sabah and Sarawak are treated differently from the rest of the States in Peninsular Malaysia and the reason for this was that the formation of Malaysia comes as a result of an agreement between Peninsular Malaya Sabah Sarawak Singapore and the British Colonial government - the Malaysia Agreement. The tradition of Sabah and Sarawak Christians who have for hundreds of years used the word Allah without any inter-religious problems must be respected.
Iban customary laws is only applicable to the state of Sarawak in East Malaysia while Dusun customary laws is only applicable to the state of Sabah in East Malaysia. ENACTED by the Legislature of the State of Sabah as follows. Peninsular Muslims must not try to dictate to Sabah and Sarawak how to live inter-communally.
Parliamentary seats equally amongst Malaya Sabah Sarawak. The state has had a trading relationship with China starting from the 14th century AD. The major employment laws are Employment Act 1955 Sabah Labour Ordinance amended 2005 Sarawak Labour Ordinance amended 2005 National Wages Consultative Council Act 2011 Children and Young persons Employment Act 1966 Workers Minimum Standards of Housing and Amnesties Act 1990 Weekly Holydays Act 1950 Mini mum Retirement Age Act 2012 The purposes of each law.
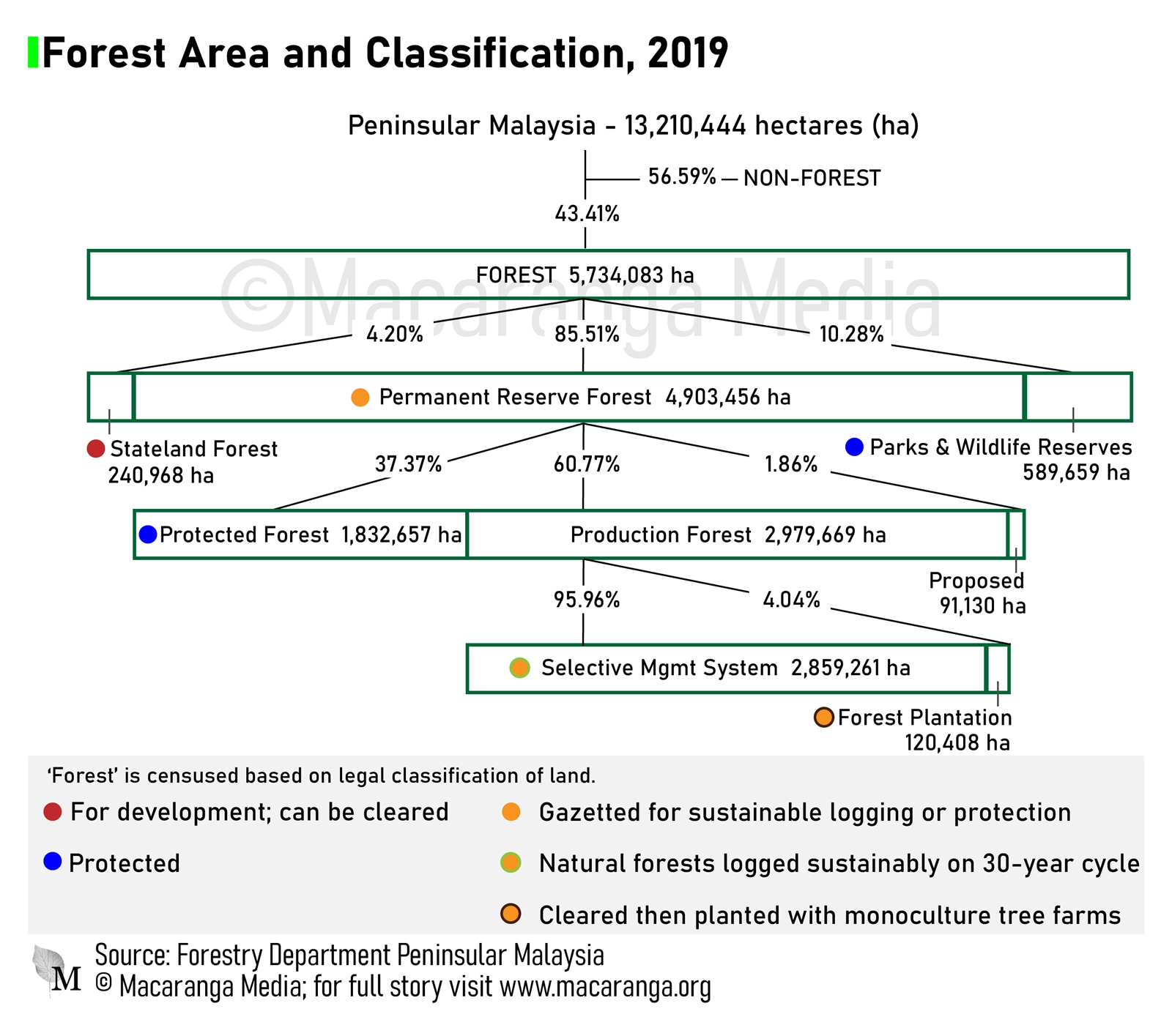
Unlike Peninsular Malaysia and Sabah the Permanent Forest Estate in Sarawak equivalent to Peninsulas Permanent Reserved Forests and Sabahs Forest Reserves while being referred to as the former in federal classification also showed a corresponding decline falling from 478 million hectares in 2005 to 421 million hectares in 2018 a reduction of 057 million hectares. Instead on this issue Peninsular Malaysians must learn from Sabah and Sarawak. Although there also seems to be a notable difference between the number of native parents required for qualification between Sabah and Sarawak states the most distinct difference between the state laws lies in the religious affiliation that comes from the peninsular regulations.
2 of 1968 An Enactment to repeal and replace the law relating to the preservation of forests and the regulation and control of dealings in forest produce. East Malaysia also known as Sabah Sarawak and Labuan or Malaysian Borneo is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo the worlds third largest island. If Allah can be used among Christians in Sabah and Sarawak it shows that there is really no legal rationale for banning the use of the word by Christians in the first place.
Prior to this the Minimum Wages Order 2016 decided that the minimum wage was about RM1000 a month in Peninsular Malaysia and RM920 a month in Sabah Sarawak. Labuan is an island in a small archipelago of the coast of Sabah. Adat Temenggong is customary laws based on Islamic principles and is applicable to all the other states in West Malaysia except Negeri Sembilan.
Sabah and Sarawak still retains a relatively higher degree of autonomy compared to the peninsular states in areas such as immigration some control over state revenue and legislative power over land and local government. And for matters connected therewith and incidental thereto.